Ecosystem
什么是Ecosystem
weroll是面向微服务架构开发而生的。对于大中型的复杂应用或平台,通常由多个子系统组成,而开发者经常需要在子系统间进行数据交互。
weroll/eco/Ecosystem 对象用来实现在多个weroll应用之间进行数据交互的需求。Ecosystem 的工作机理是通过HTTP连接在weroll应用之间进行双向数据通讯,通过配置即将多个应用连接起来,构建成为一个生态系统,因此我们管它叫做 Ecosystem:
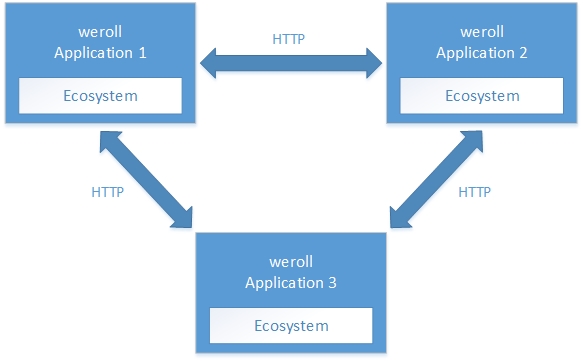
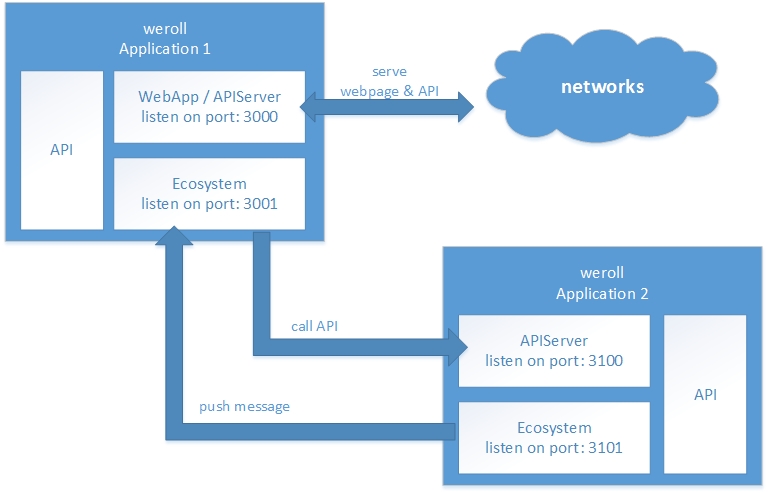
Ecosystem 会建立一个新的HTTP服务器(使用一个新的端口),作为数据接收器;同时它使用 request 对象发出HTTP请求来实现数据推送。Ecosystem 可以像客户端一样直接调用另一个weroll应用的API,也可以像消息订阅一样侦听由其他weroll应用主动推送过来的消息数据。如下图所示:
开始使用Ecosystem
首先需要在setting.js中对Ecosystem进行配置:
/* %WORKSPACE%/Application1/server/config/%ENV%/setting.js */
module.exports = {
host: "192.168.1.10",
port: 3000, //WebApp or APIServer will use this port
/* so the api gateway of this application is: 192.168.1.10:3000 */
...
ecosystem: {
name: "app1", //define the name of Ecosystem for this application
port: 3001, //Ecosystem will use this port
servers : {
//define other weroll applications
"app2" : {
message:"192.168.1.10:3101", //define the address of the Ecosystem in app2
api:"192.168.1.10:3100/api" //define the API gateway of app2
},
//more weroll application
"app3" : {
message:"app3-msg.jay.com", //or use domain path
api:"app3-api.jay.com/api"
}
}
}
}
通过以上配置,Application1这个项目(使用app1作为标识)可以同时和另外2个weroll应用进行双向数据通讯。
对于app2这个应用,我们可以这样进行配置:
/* %WORKSPACE%/Application2/server/config/%ENV%/setting.js */
module.exports = {
host: "192.168.1.10",
port: 3100, //WebApp or APIServer will use this port
/* so the api gateway of this application is: 192.168.1.10:3100 */
...
ecosystem: {
name: "app2", //define the name of Ecosystem for this application
port: 3101, //Ecosystem will use this port
servers : {
//define other weroll applications
"app1" : {
message:"192.168.1.10:3001", //define the address of the Ecosystem in app1
api:"192.168.1.10:3000/api" //define the API gateway of app1
}
}
}
}
通过以上配置,Application2这个项目(使用app2作为标识)允许和app1进行双向数据通讯。因为没有配置app3的信息,所以app2无法和app3进行通讯。
配置完成后,需要在程序入口脚本中初始化Ecosystem:
// ./main.js
//some initialize works...
app.addTask(function(cb) {
//create and start a web application
var webApp = require("weroll/web/WebApp").start(Setting, function(webApp) {
/* setup Ecosystem */
var Ecosystem = require("weroll/eco/Ecosystem");
Ecosystem.init();
/* Ecosystem is ready to go! */
cb();
});
});
//more initialize works...
app.run();
初始化之后,Ecosystem 即成为一个全局对象,可以在任意代码中使用而不需要require导入。
调用API
使用 Ecosystem.callAPI 方法即可调用其他weroll应用的API,示例代码如下:
/* Application1 (app1) invokes API of app2 */
//callback
//Ecosystem.callAPI(target, api_name, data, [ callback ])
Ecosystem.callAPI("app2", "system.now", { format:1 }, function(err, data) {
if (err) return console.error(err);
console.log("app2 response API: ", data);
});
//Promise
Ecosystem.callAPI("app2", "system.now", { format:1 }).then(function(data) {
console.log("app2 response API: ", data);
}).catch(function(err) {
console.error("Error code: ", err.code, " msg: ", err.msg);
});
//async & await
async function() {
var data = await Ecosystem.callAPI("app2", "system.now", { format:1 });
console.log("app2 response API: ", data);
}
如果你恐惧function总是需要传递很多参数,也可以这样写:
Ecosystem.TARGET_APP_NAME.callAPI(api_name, data, [callback])
/* Application1 (app1) invokes API of app2 */
var data1 = await Ecosystem.app2.callAPI("system.now", { format:1 });
console.log("app2 response API: ", data1);
/* invokes API of app3 */
var data2 = await Ecosystem.app3.callAPI("user.hello", { name:"Jay" });
console.log("app3 response API: ", data2);
订阅和推送消息
使用 Ecosystem.callAPI 可以主动推送消息给其他weroll应用,或订阅其他weroll应用的推送。示例代码如下:
/* Application1 (app1) */
Ecosystem.onServeReady("app2", function() {
//app2 application is registered into Ecosystem of app1
//listen message from app2
Ecosystem.listen("app2", "talk", function(data) {
console.log("app2 talk to you: ", data); //echo { msg: 'hello!' }
});
//or
Ecosystem.app2.listen("talk", function(data) {
console.log("app2 talk to you: ", data); //echo { msg: 'hello!' }
});
});
/* Application1 (app2) */
//send message to app1
//Ecosystem.TARGET_APP_NAME.fire(event, data)
Ecosystem.app1.fire("talk", { msg:"hello!" });
当我们在构建一个复杂的微服务生态系统时,某些情况下可能并不清楚消息是来自哪个应用的;或者某个应用需要同时侦听多个应用推送的同一类消息,因此也就难以进行消息订阅侦听。Ecosystem.listenAll 方法可以侦听来自任何应用的消息,而不需要知道应用的名字,示例代码如下:
/* Application1 (app1) */
//app1 will receive message from app2 and app3, or other weroll applications
Ecosystem.listenAll("talk", function(data, sender) {
console.log(sender + " talk to you: ", data);
//1. echo "app2 talk to you: hello!"
//2. echo "app3 talk to you: hi~"
});
/* Application2 (app2) */
//send message to app1
Ecosystem.app1.fire("talk", { msg:"hello!" });
/* Application3 (app3) */
//send message to app1
Ecosystem.app1.fire("talk", { msg:"hi~" });